# A tibble: 4 × 6
degree `2011` `2012` `2013` `2014` `2015`
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 AB2 NA 1 NA NA 4
2 AB 2 2 4 1 3
3 BS2 2 6 1 NA 5
4 BS 5 9 4 13 10Data Joining
Lecture 7
Announcements/Reminders
Office hours are today from 1:00-3:00 on Zoom
-
AE04… that was a lot
The first 3 parts that we did in class are what are important!
The rest is a good exercise in data vis.
Questions about lab?
Outline
Last Time: Started learning about data transformation!
-
Today:
Review from last time
Joining data (working with multiple data frames)
Review: Pivot Longer
How do we go from this…
…to this?
# A tibble: 56 × 3
degree year n
<fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 AB2 2011 NA
2 AB2 2012 1
3 AB2 2013 NA
4 AB2 2014 NA
5 AB2 2015 4
# ℹ 51 more rowsReverse It: Pivot Wider
How do we get back to this…
# A tibble: 4 × 6
degree `2011` `2012` `2013` `2014` `2015`
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 AB2 NA 1 NA NA 4
2 AB 2 2 4 1 3
3 BS2 2 6 1 NA 5
4 BS 5 9 4 13 10… from this?
# A tibble: 56 × 3
degree year n
<fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 AB2 2011 NA
2 AB2 2012 1
3 AB2 2013 NA
4 AB2 2014 NA
5 AB2 2015 4
# ℹ 51 more rowsRecap: Pivot Functions
Pivot longer…
data_set |>
pivot_longer(
cols = colums_to_move,
names_to = "var_for_column_names",
values_to = "var_for_values"
)… or wider
data_set |>
pivot_wider(
names_from = var_with_cols,
values_to = var_with_vals
)Joining Data
Joining Data
What happens if we want information from two different data sets?
Joining Data: Sample Scenario
population# A tibble: 217 × 3
country year population
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan 2022 41129.
2 Albania 2022 2778.
3 Algeria 2022 44903.
4 American Samoa 2022 44.3
5 Andorra 2022 79.8
6 Angola 2022 35589.
7 Antigua and Barbuda 2022 93.8
8 Argentina 2022 46235.
9 Armenia 2022 2780.
10 Aruba 2022 106.
# ℹ 207 more rowsWe want to know about population in different continents.
We could use mutate to create a continent variable, but that would be terrible….
Joining Data: Sample Scenario
population# A tibble: 217 × 3
country year population
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan 2022 41129.
2 Albania 2022 2778.
3 Algeria 2022 44903.
4 American Samoa 2022 44.3
5 Andorra 2022 79.8
6 Angola 2022 35589.
7 Antigua and Barbuda 2022 93.8
8 Argentina 2022 46235.
9 Armenia 2022 2780.
10 Aruba 2022 106.
# ℹ 207 more rowscontinent# A tibble: 285 × 4
entity code year continent
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 Abkhazia OWID_ABK 2015 Asia
2 Afghanistan AFG 2015 Asia
3 Akrotiri and Dhekelia OWID_AKD 2015 Asia
4 Aland Islands ALA 2015 Europe
5 Albania ALB 2015 Europe
6 Algeria DZA 2015 Africa
7 American Samoa ASM 2015 Oceania
8 Andorra AND 2015 Europe
9 Angola AGO 2015 Africa
10 Anguilla AIA 2015 North America
# ℹ 275 more rowsJoining: Example Data
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
Joining: Left Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
left_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
| 3 | X3 | NA |
Joining: Left Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
left_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
| 3 | X3 | NA |
Joining: Right Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
right_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
| 4 | NA | Y4 |
Joining: Right Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
right_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
| 4 | NA | Y4 |

Joining: Full Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
right_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
| 3 | X3 | NA |
| 4 | NA | Y4 |
Joining: Full Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
right_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
| 3 | X3 | NA |
| 4 | NA | Y4 |

Joining: Inner Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
inner_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
Joining: Inner Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
inner_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |

Joining: Semi Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
semi_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
Joining: Semi Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
semi_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |

Joining: Anti Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
anti_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 3 | X3 |
Joining: Anti Join
df_X
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
anti_join(df_X, df_Y)
| id | X |
|---|---|
| 3 | X3 |

Summary of Join Types
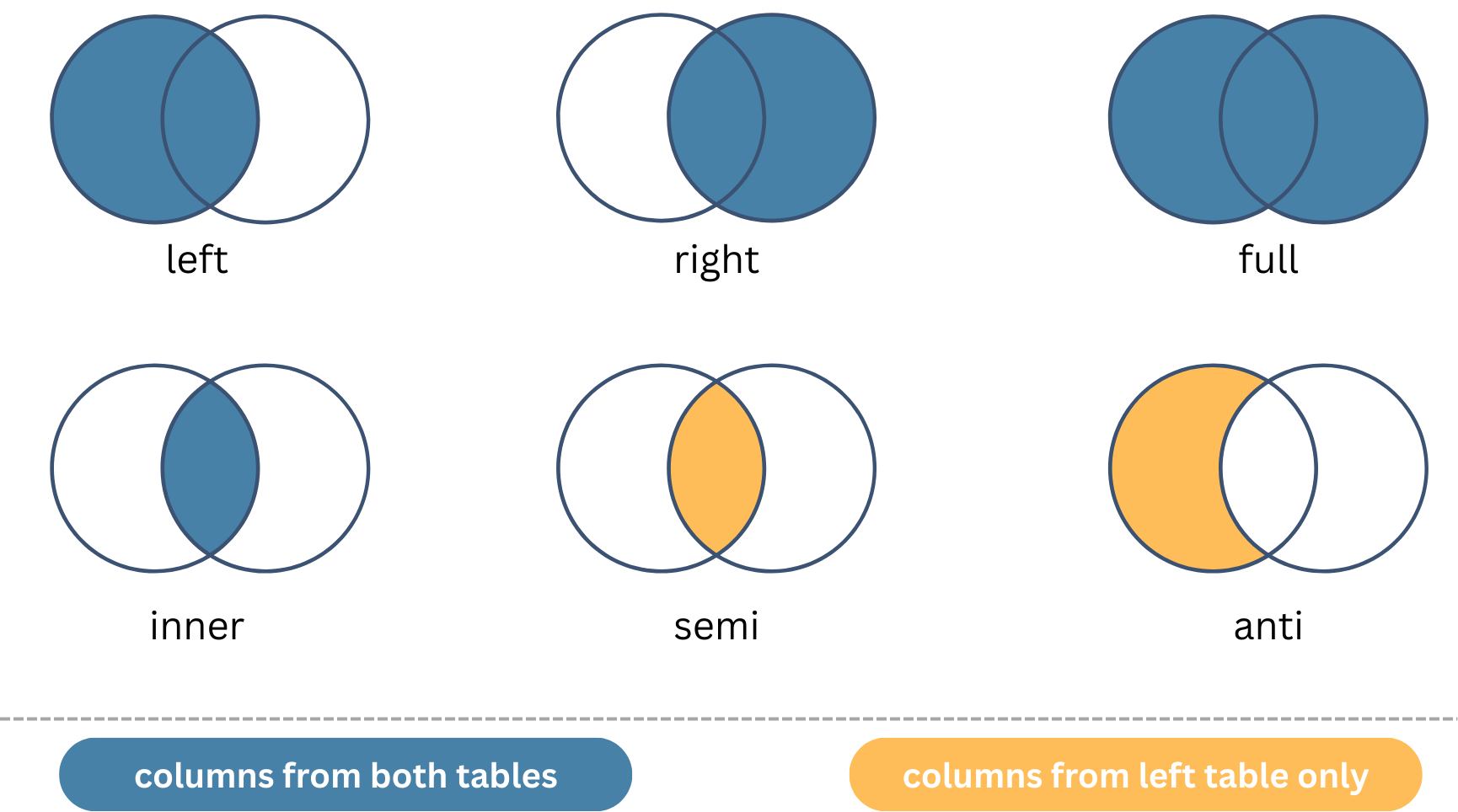
More Notes on Join
In the following examples, I use left_join()
The same concept holds for other types of joins!
Idea: how do we specify which columns we want to join with?
Join: Which columns?
How can I specify which column to join by?
df_X
| id_X | X |
|---|---|
| 1 | X1 |
| 2 | X2 |
| 3 | X3 |
df_Y
| id_Y | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | Y1 |
| 2 | Y2 |
| 4 | Y4 |
goal: left join
| id_X | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X1 | Y1 |
| 2 | X2 | Y2 |
| 3 | X3 | NA |
left_join(df_X, df_Y,
by = join_by(id_X == id_Y))What about the pipe?
The following two pieces of code are equivalent:
left_join(df_X, df_Y,
by = join_by(id_X == id_Y))df_X |> left_join(df_Y,
by = join_by(id_X == id_Y))Let’s save!
Most often, you will want to save the result of a join to a new data frame.
df_X_Y <- df_X |> left_join(df_Y,
by = join_by(id_X == id_Y))Your Turn
What is the result?
AE 07
Goal: Do a join!!!
Data
population# A tibble: 217 × 3
country year population
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan 2022 41129.
2 Albania 2022 2778.
3 Algeria 2022 44903.
4 American Samoa 2022 44.3
5 Andorra 2022 79.8
6 Angola 2022 35589.
7 Antigua and Barbuda 2022 93.8
8 Argentina 2022 46235.
9 Armenia 2022 2780.
10 Aruba 2022 106.
# ℹ 207 more rowscontinent# A tibble: 285 × 4
entity code year continent
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 Abkhazia OWID_ABK 2015 Asia
2 Afghanistan AFG 2015 Asia
3 Akrotiri and Dhekelia OWID_AKD 2015 Asia
4 Aland Islands ALA 2015 Europe
5 Albania ALB 2015 Europe
6 Algeria DZA 2015 Africa
7 American Samoa ASM 2015 Oceania
8 Andorra AND 2015 Europe
9 Angola AGO 2015 Africa
10 Anguilla AIA 2015 North America
# ℹ 275 more rows